An SMTP relay server is one of the powerful ways of routing email messages through a trusted third-party server. This method especially helps in sending bulk or transactional emails from applications, which would have high chances of getting delivered and will never get marked as spam against your emails. Here’s a guide to know about what an SMTP relay is, how to set it up, and how to use it.
What is SMTP Relay?
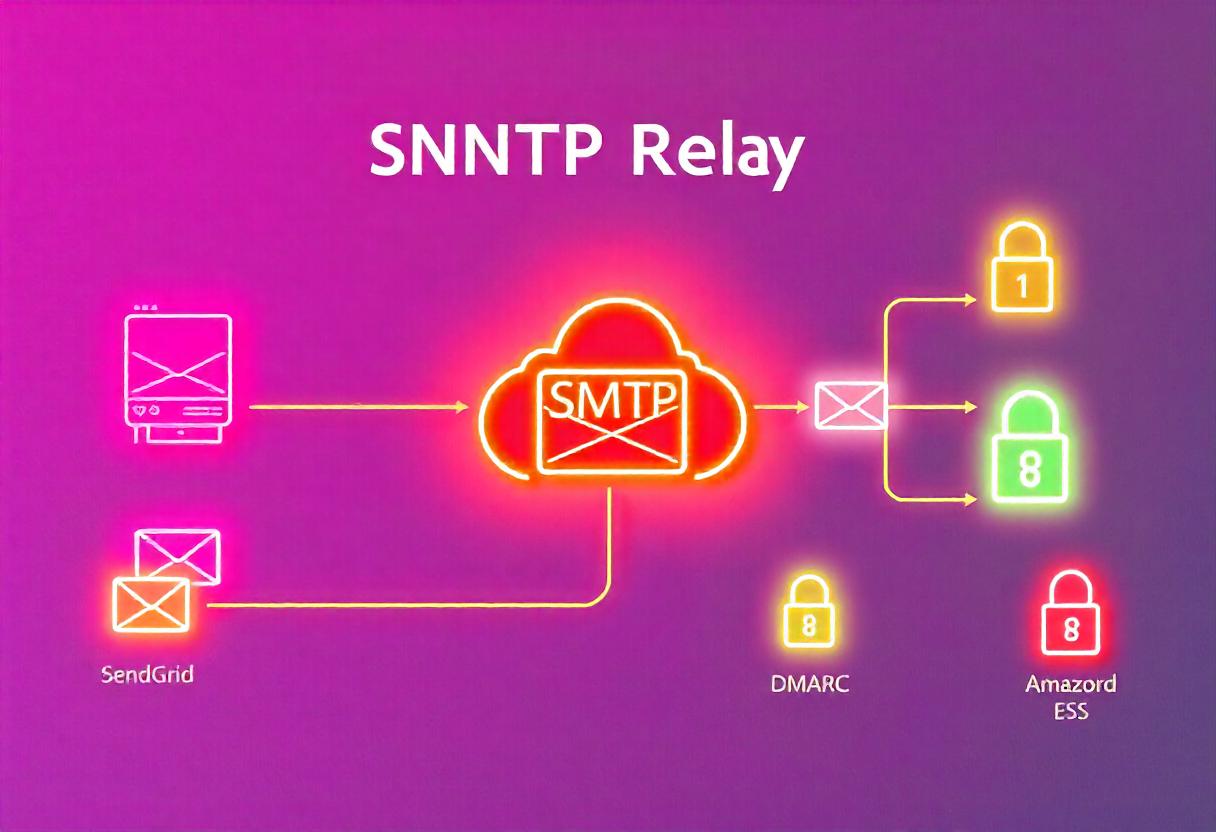
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) relay is the act of forwarding mail through an intermediate server so that it reaches the actual destination. Instead of trying to send emails straight out from your own mail server, SMTP relay makes room for a third party, which handles the transmission in return, offering benefits, such as:
- Improve Deliverability: Trusted SMTP relays develop reputations with Internet service providers that can work toward avoiding spam filters.
- Reduced Server Load: Since the process of sending emails is offloaded to an external server, your infrastructure is not burdened with this process.
- Increased Security: Reputable SMTP relay services will have built-in security features such as encryption and authentication.
When to Use SMTP Relay
SMTP relays are often used for the following purposes:
- Transactional Emails: Sending automated emails such as order confirmations, password resets, and notifications.
- Bulk Email Campaigns: For marketing emails where you need to send emails to a large subscriber list.
- Sending from Applications: An application needs to send emails on behalf of the users, for example, alerts or notifications.
Setup an SMTP Relay
Depending on your hosting environment, setting up an SMTP relay varies a little bit. The rest of this article includes general steps to set up an SMTP relay on your own dedicated server or from a service provider for using an SMTP relay.
Choose an SMTP Relay Provider
In choosing an SMTP relay, here are some popular service providers:
- SendGrid
- Amazon SES
- Mailgun
- Google SMTP Relay – this is if you will be using G Suite services
- Microsoft Office 365 SMTP Relay
Step 1: Choose an Email Relay
Choose an email relay whose feature and pricing is acceptable based on your volume, budget, and feature requirement.
Step 2: Get SMTP Credentials
After subscribing, you get the SMTP credentials that will have:
- SMTP Server Address: An example will be smtp.sendgrid.net
- SMTP Port: Usually 25, 465, or 587 depending on which type of encryption is in use
- Username and Password: To authenticate with the server
Step 3: Configure SMTP Settings
Now you configure your application or your email client using the SMTP settings provided by your relay provider. Here is how to do it:
- Open your email client or application, navigate to the outgoing mail (SMTP) server settings.
- Enter the SMTP server address and port assigned by your provider.
- Enter username and password, usually the authentication credentials represented by your account email and password or special API key.
- Enable SSL/TLS: If permitted by your provider, turn on SSL or TLS encryption to encrypt email delivery.
Step 4: Test SMTP Relay Configuration
After configuring your SMTP settings, you want to test the configuration for sending emails correctly using the relay. You can quickly do this by testing:
- Sending a Test Email: From your application or client, send a test email to a known recipient.
- Verify Delivery: Check the recipient’s inbox as well as the inbox in your server for an accurate delivery verification. Moreover, most of the providers have a dashboard, showing email logs that come in handy with this task.
Best Practice When Using SMTP Relay
- 1. Clean Your Email List: Do not send any emails to unknown addresses and non-active recipients to reduce bounces from spam boxes and other boxes as your sender reputation will drop drastically. Clean up and verify your list. Monitor the provider’s analytics to get better rates of bounces, open rates, and other unsubscribe rates, thus sending better campaigns next time based on a good practice.
- 2. Do Not Send Too Many SMTP Relays: A lot of SMTP relay would get throttled, therefore avoid usage limits set in your provider to achieve full deliverability.
- 3. Setup SPF, DKIM, and DMARC: This protocol also makes your emails better, improving security and its level of trustworthiness such that there is a minimum likelihood it may end up in your spam folders.
Troubleshooting SMTP Relay Issues
If your SMTP relay isn’t performing to your level of expectation, there might be several reasons for the same:
- Correct Credentials: Have a recheck of your SMTP server address and port, username, and password.
- Firewall Issues: If you have a firewall, ensure that it’s configured to allow outgoing traffic on your SMTP port.
- SPF/DKIM/DMARC Configuration: Ensure that these records are correctly set up for your domain. Misconfigurations here can cause email rejections.
Conclusion
With the SMTP relay, you have an assured way of getting through with reliable email delivery, lessening the load on your own servers. This includes transactional emails, application notifications, and even marketing campaigns. Using an SMTP relay service can thus boost deliverability and security when sending emails. From these setup steps and best practices, you can establish a suitable SMTP relay to achieve effective email communication for your business.
FAQs
Q1. Do I use the SMTP relay for any intra-network e-mails?
Typically, intra-network should be fine with the relays that already exist within the same network in place. External emails may need SMTP, or for a higher delivery rate.
Q2. Are free SMTP relays available?
Yes, some have free SMTP relays which are fine for lighter usages but are otherwise usually paid services. For example, the SendGrid free plan works decently for usage of <10%.
Q3. Can I use the SMTP relay for sending marketing emails in bulk?
Yes, SMTP relays are often used to send bulk emails. Nonetheless, abide by email marketing best practices and the CAN-SPAM rules.